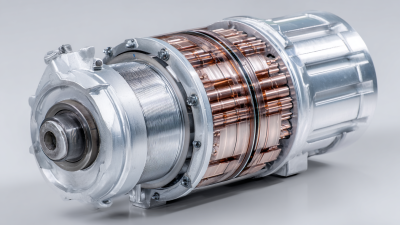
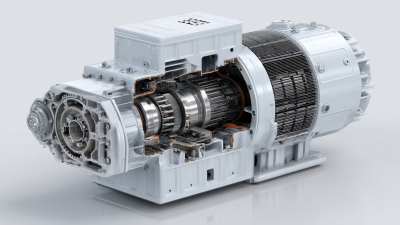
A Permanent Synchronous Motor (PSM) is a critical component in modern electrical engineering, known for its efficiency and reliability in providing precise control in various applications. As highlighted by industry expert Dr. Emily Larson, "The Permanent Synchronous Motor represents the pinnacle of motor technology, combining high efficiency with performance stability." This technology has gained significant traction due to its ability to maintain synchronous speed under varying loads, which is essential for applications demanding constant speed and torque.
The operating principle of a Permanent Synchronous Motor involves the use of permanent magnets in the rotor, which interact with the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator. This interaction not only ensures precise synchronization with the power supply frequency but also minimizes energy losses, making PSMs an attractive option for industries ranging from robotics to renewable energy systems. As we delve deeper into the functionalities and advantages of Permanent Synchronous Motors, it is essential to understand how their design and operation contribute to their exceptional performance in today’s technologically advanced landscape.
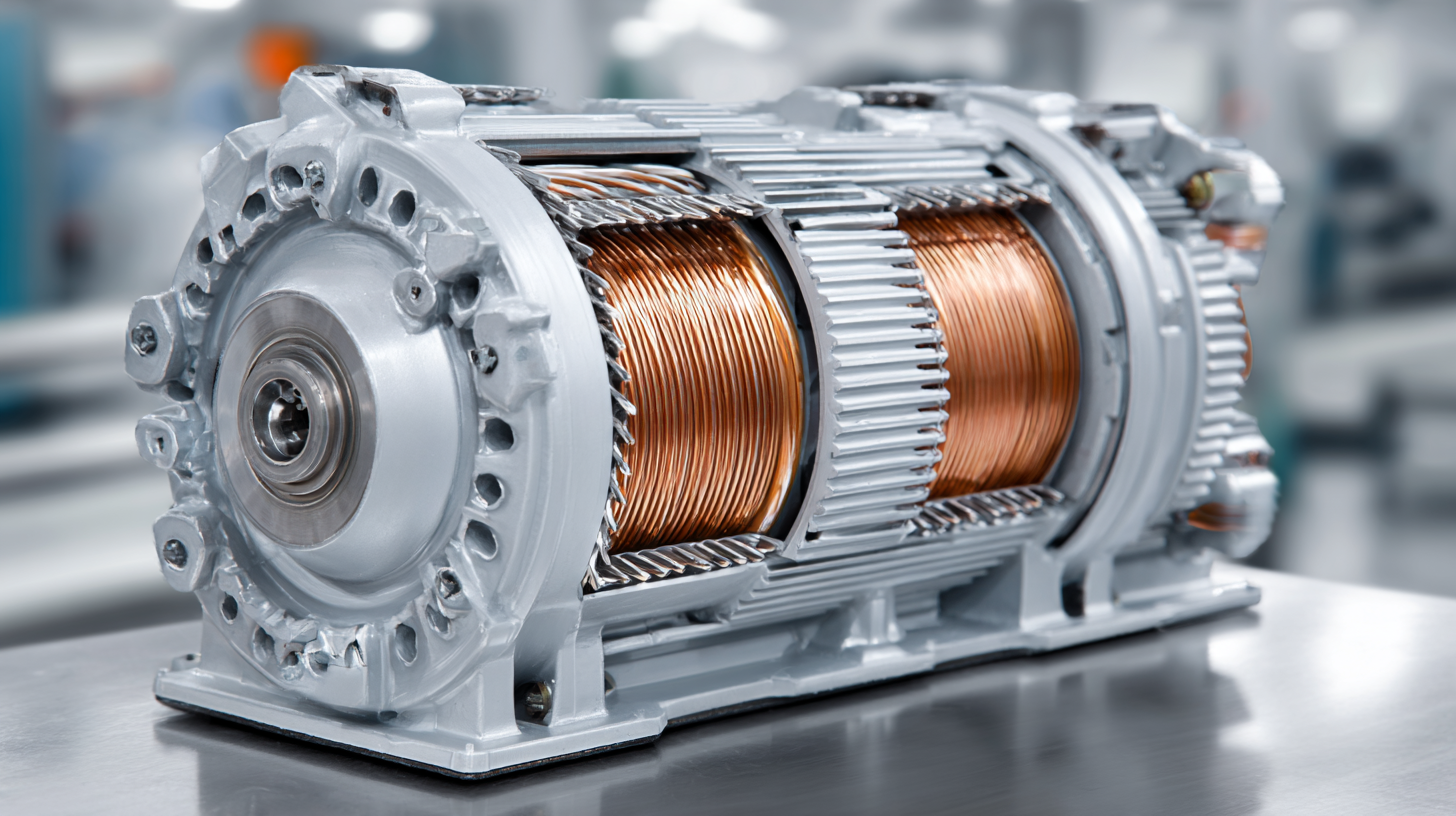
Permanent synchronous motors (PSMs) are a type of electric motor that operate using permanent magnets and require an alternating current (AC) supply. Unlike induction motors, PSMs maintain synchronous speed with the rotating magnetic field, ensuring a precise relationship between the speed of the rotor and the stator's magnetic field. This feature enables them to deliver high efficiency and consistent performance across various applications, from industrial machinery to household appliances.
The working principle of permanent synchronous motors revolves around the interaction between the magnetic field generated by the stator and the rotor's permanent magnets. When AC voltage is applied to the stator windings, it creates a rotating magnetic field. The rotor, which is equipped with permanent magnets, aligns with this field due to the magnetic attraction. As the rotating magnetic field moves, the rotor follows, thereby generating mechanical power. This synchronous operation allows for efficient torque generation and reduces energy losses, making PSMs a popular choice in applications where precise control and reliability are paramount.
Permanent synchronous motors (PSMs) incorporate several key components that define their operation and efficiency. At the heart of these motors are the permanent magnets that create a constant magnetic field, which interacts with the stator windings to produce rotational motion. The rotor of a permanent synchronous motor typically consists of high-energy density magnets, ensuring strong magnetic coupling and improving overall performance. Additionally, the stator is wound with coils that are energized to generate an alternating magnetic field, synchronizing with the rotor's magnetic field and allowing for seamless motor operation.
In the context of advancements in motor technology, the integration of IoT and AI is poised to enhance the functionality of permanent synchronous motors significantly. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and control, optimizing motor efficiency and performance based on varying operational demands. With the growing emphasis on smart and connected vehicles, the demand for advanced permanent synchronous motors is expected to rise, fostering innovations such as lightweight designs and multiphysics coupling analysis. This evolution in motor technology not only addresses the challenges of energy efficiency but also supports the broader trends shaping the future of the automotive industry.
This chart illustrates the efficiency of the key components of permanent synchronous motors. The stator exhibits the highest efficiency, followed by the rotor. The shaft, exciter, and bearings show progressively lower efficiency, indicating areas for potential improvement in motor design.
Permanent synchronous motors (PSMs) are widely utilized in various applications due to their efficiency and reliability. The basic principle of operation hinges on the interaction between the motor's permanent magnets and the stator's rotating magnetic field. When an alternating current flows through the stator windings, it generates a magnetic field that synchronizes with the rotor's magnetic field created by the permanent magnets. This synchronization results in a torque that drives the rotor at synchronous speed, eliminating slip and enabling precise speed control. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global permanent magnet motor market is expected to reach $21.85 billion by 2026, indicating the growing adoption of PSMs in sectors such as manufacturing and automotive.
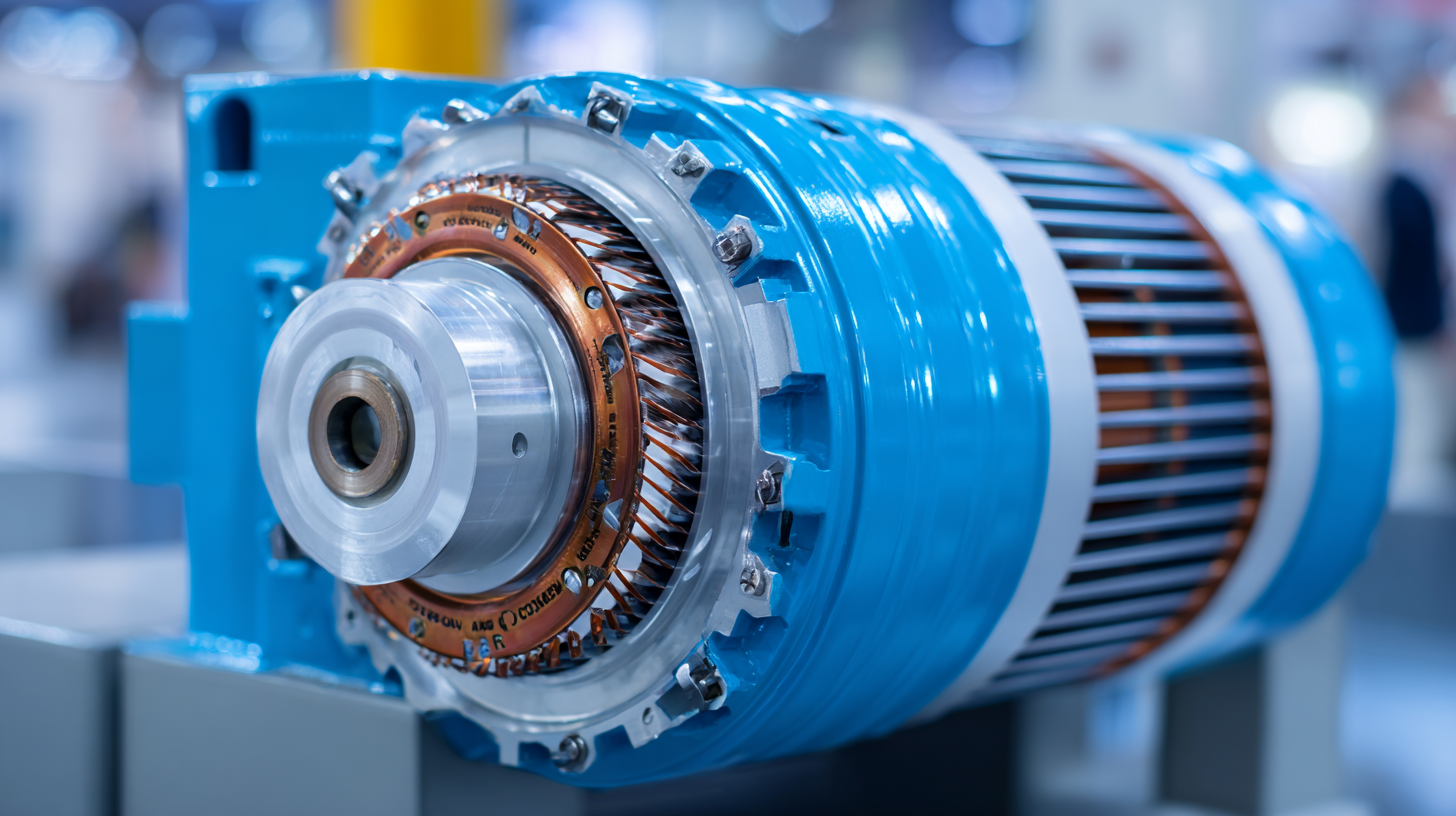
The operational efficiency of permanent synchronous motors is significantly higher than that of traditional induction motors. This is evidenced by their ability to maintain high torque at low speeds, which is particularly advantageous in applications like electric vehicles and industrial automation. Industry research indicates that PSMs can achieve efficiencies exceeding 90%, a crucial factor contributing to their increased deployment in energy-sensitive applications. Moreover, the use of high-energy magnets, such as neodymium-iron-boron, enhances performance, allowing PSMs to maintain compact designs while delivering substantial power output. This makes them a compelling choice for modern technological advancements.
 Permanent synchronous motors (PSMs) have gained prominence in modern applications due to their distinct advantages over traditional induction motors. One significant advantage is their high efficiency. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), PSMs can achieve efficiencies exceeding 95%, which not only reduces energy consumption but also lowers operational costs in industries such as manufacturing and energy. This makes them an ideal choice for applications requiring prolonged operation at high loads.
Permanent synchronous motors (PSMs) have gained prominence in modern applications due to their distinct advantages over traditional induction motors. One significant advantage is their high efficiency. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), PSMs can achieve efficiencies exceeding 95%, which not only reduces energy consumption but also lowers operational costs in industries such as manufacturing and energy. This makes them an ideal choice for applications requiring prolonged operation at high loads.
Another key benefit of permanent synchronous motors is their superior torque characteristics. As reported by the United States Department of Energy (DOE), PSMs produce a consistent torque across various speeds, leading to smoother operation and enhanced performance in precision-driven tasks. This characteristic is particularly valuable in robotics and conveyors, where accurate speed control is critical. Moreover, the growing emphasis on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints has led to increased adoption of PSMs, as they offer lower emissions and can be integrated with renewable energy sources, further enhancing their appeal in modern industrial applications.
The field of Permanent Synchronous Motor (PSM) technology is experiencing rapid advancements, driven by the demands for energy efficiency and improved performance. Recent industry reports indicate that the global permanent magnet motor market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.5% from 2023 to 2030, reaching approximately $30 billion by the end of the decade. This growth can be attributed to increased automation, adoption of electric vehicles, and renewable energy applications, where PSMs play a critical role in enhancing operational efficiency.
Future trends in PSM technology are focusing on the integration of advanced materials and smart technologies. Innovations such as the use of high-energy-density magnets, improved rotor designs, and integration with IoT for real-time monitoring are all on the rise. According to a study by the International Electrotechnical Commission, implementing advanced manufacturing techniques could reduce production costs by up to 20%. These innovations are likely to further boost the adoption of synchronous motors across various industries, from manufacturing to renewable energy systems.
Tips: When considering the implementation of Permanent Synchronous Motors, evaluate the potential for energy savings and ROI based on current operational costs. Additionally, stay informed about technology trends and seek partnerships with manufacturers focused on developing cutting-edge PSM technologies.
| Parameter | Description | Current Trends | Future Innovations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency than induction motors | Focus on improved energy efficiency standards | Integration with renewable energy systems |
| Control Methods | Constant speed operation with feedback control | Adoption of vector control technology | Use of AI for predictive control and optimization |
| Applications | Used in industrial drives and robotics | Growing demand in electric vehicles | Expansion in HVAC systems and renewable energy sectors |
| Material Advances | Use of high-performance magnets | Research into lightweight composite materials | Development of new magnet manufacturing techniques |
| Market Trends | Increasing adoption in automation | Growth in consumer electronics | Emerging markets for IoT and smart systems |